2024 United States Demographics | Comprehensive Overview
Data and insights for the United States, including population, age & gender distribution, race & ethnicity, median & household income distribution, property value distribution, educational attainment, health insurance coverage, nativity & citizenship, commuting & transportation, employment, veteran service, poverty & income and SNAP/food stamp recipients. Based on 2024 American Community Survey Estimates.
United States Key Demographic Statistics (2024 Estimates)
Key demographic statistics summarized from the U.S. Census Bureau's 2024 American Community Survey (ACS).
Source: U.S. Census Bureau, 2024 American Community Survey (ACS) Estimates
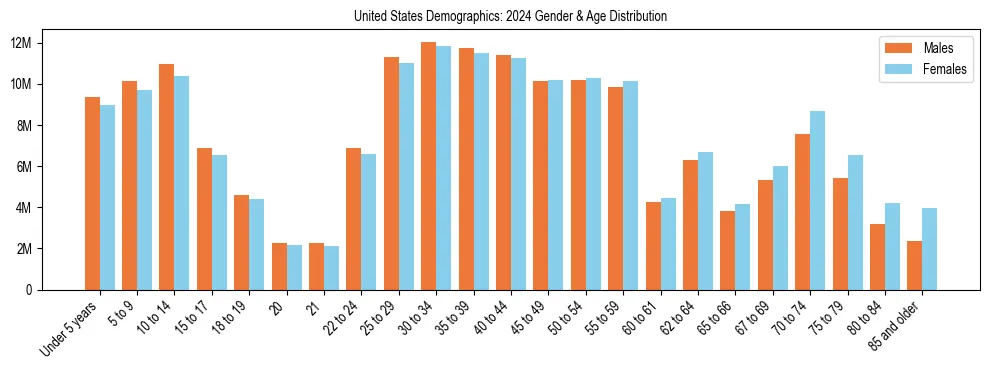
United States Demographics: Age & Gender Distribution (2024)
Key Demographic Indicators for United States
The following statistics highlight the United States population and median age, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Total Population
- 340,110,990
- Median Age (Total)
- 39.2 years
- Median Age (Male)
- 38.1 years
- Median Age (Female)
- 40.3 years
United States Population Age Distribution
| Age Cohort | Share of Population |
|---|---|
| Under 5 years | 5.40% |
| 5–17 years (Children) | 16.04% |
| 18–24 years (Young Adults) | 9.19% |
| 25–34 years | 13.58% |
| 35–54 years | 25.52% |
| 55–64 years | 12.26% |
| 65 years and over (Seniors) | 18.01% |
Dependency Ratios Analysis
- Total Dependency Ratio
- 65.15
- Youth Dependency Ratio
- 35.41 Population under 18 relative to working age (18-64).
- Old-Age Dependency Ratio
- 29.74 Population 65+ relative to working age (18-64).
A higher ratio indicates a greater financial and social burden on the working population to support non-working age groups.
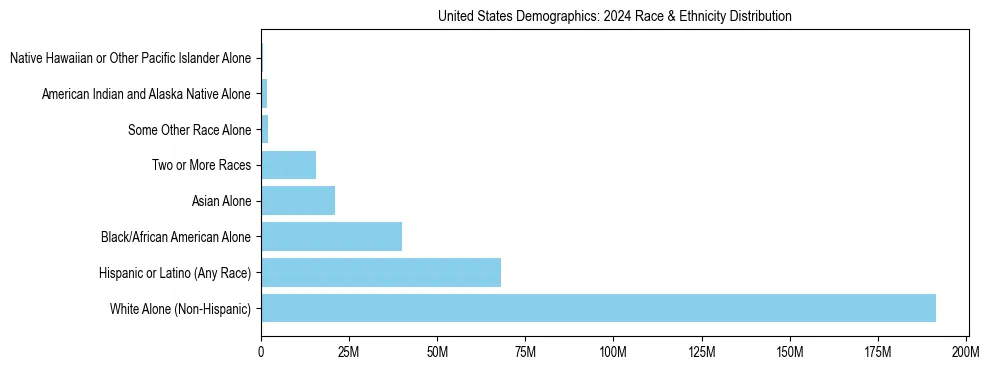
United States Demographics: Racial and Ethnic Composition (2024)
Diversity & Cultural Composition of United States
The racial makeup and ethnic composition of the United States are detailed below, drawing from the U.S. Census Bureau's 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Diversity Index Score
- 62.36
- Diversity Tier
- high
- Definition
- The probability that two individuals chosen at random will be from different racial or ethnic groups.
United States Population by Race/Ethnicity
| Racial/Ethnic Group | Percentage |
|---|---|
| White Alone (Non-Hispanic) | 56.27% |
| Hispanic or Latino (Any Race) | 20.00% |
| Black/African American Alone | 11.75% |
| Asian Alone | 6.19% |
| Two or More Races | 4.56% |
| Some Other Race Alone | 0.54% |
| American Indian and Alaska Native Alone | 0.52% |
| Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander Alone | 0.17% |
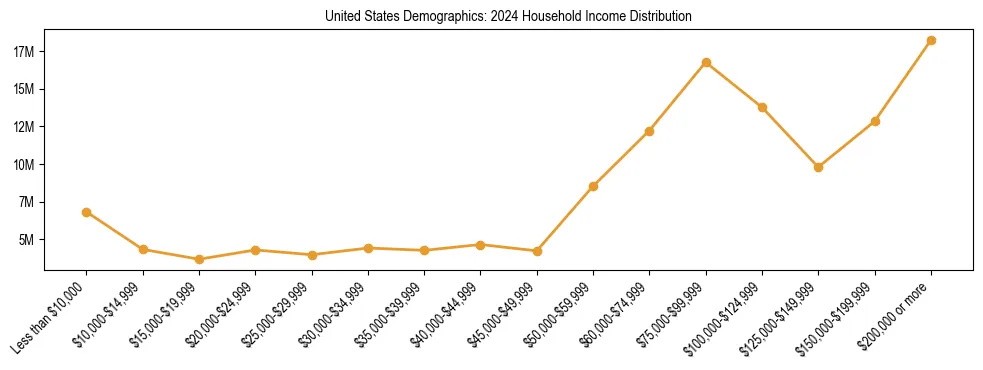
United States Economic Demographics: Household Income Statistics (2024)
Economic Snapshot for United States
The following data illustrates the financial landscape of the United States, based on the latest U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Median Household Income
- $81,604 (Adjusted for inflation)
- Total Households Analyzed
- 132,737,146
United States Household Income Distribution
| Annual Income Range | Share of Households |
|---|---|
| Less than $20,000 | 11.15% |
| $20,000 to $34,999 | 9.53% |
| $35,000 to $49,999 | 9.89% |
| $50,000 to $74,999 | 15.64% |
| $75,000 to $149,999 | 30.39% |
| $150,000 or more | 23.40% |
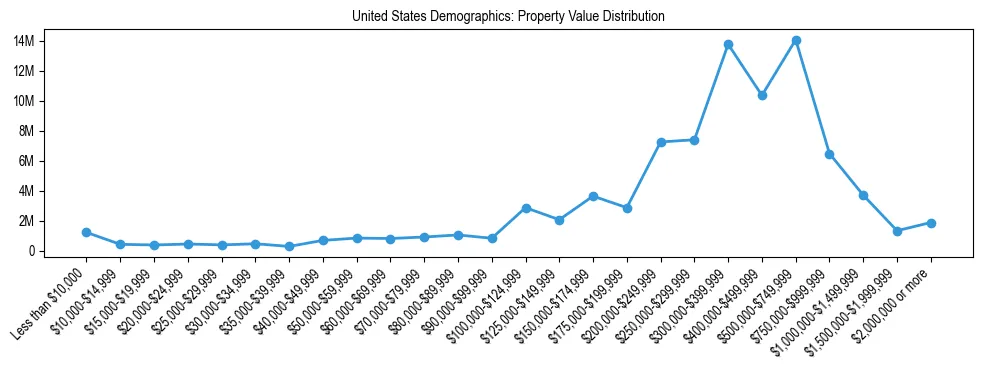
United States Real Estate Demographics: Property Values (2024)
Real Estate Market Snapshot for United States
The following data highlights the distribution of owner-occupied housing values in the United States, based on the latest U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Median Property Value
- $360,600
- Total Properties Analyzed
- 86,635,506 (Owner-occupied units)
United States Property Value Distribution
| Value Range | Share of Properties |
|---|---|
| Less than $25,000 | 2.88% |
| $25,000 to $49,999 | 2.13% |
| $50,000 to $99,999 | 5.17% |
| $100,000 to $199,999 | 13.25% |
| $200,000 to $499,999 | 44.81% |
| $500,000 to $999,999 | 28.03% |
| $1,000,000 or more | 3.72% |
United States Educational Attainment Statistics (2024)
Education Snapshot for United States
The following statistics represent the educational background of residents aged 25 and older in the United States, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- High School Graduate or Higher
- 89.92%
- Bachelor's Degree or Higher
- 36.85%
- Total Population Analyzed (25+)
- 235,910,719
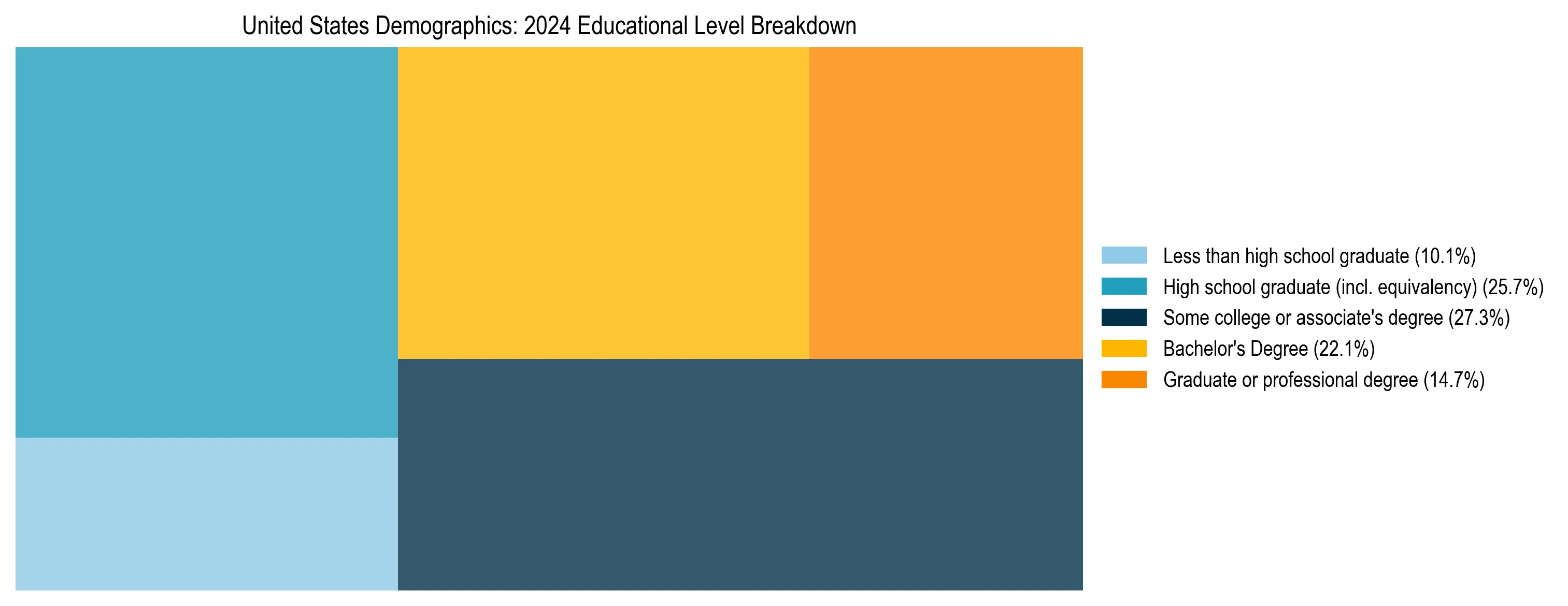
United States Education Distribution
| Education Level | Share of Population (25+) |
|---|---|
| Less than high school graduate | 10.08% |
| High school graduate (incl. equivalency) | 25.73% |
| Some college or associate's degree | 27.34% |
| Bachelor's Degree | 22.14% |
| Graduate or professional degree | 14.71% |
United States Health Insurance Coverage Statistics (2024)
Healthcare Coverage Snapshot for United States
The following data illustrates the health coverage landscape of the United States, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Overall Uninsured Rate
- 8.2%
- Total Uninsured Population
- 27,479,253
- Total Civilian Population
- 335,190,522
The uninsured rates vary significantly by demographic group. Children under 18 and seniors aged 65+ generally have higher coverage rates due to public programs like Medicaid/CHIP and Medicare.
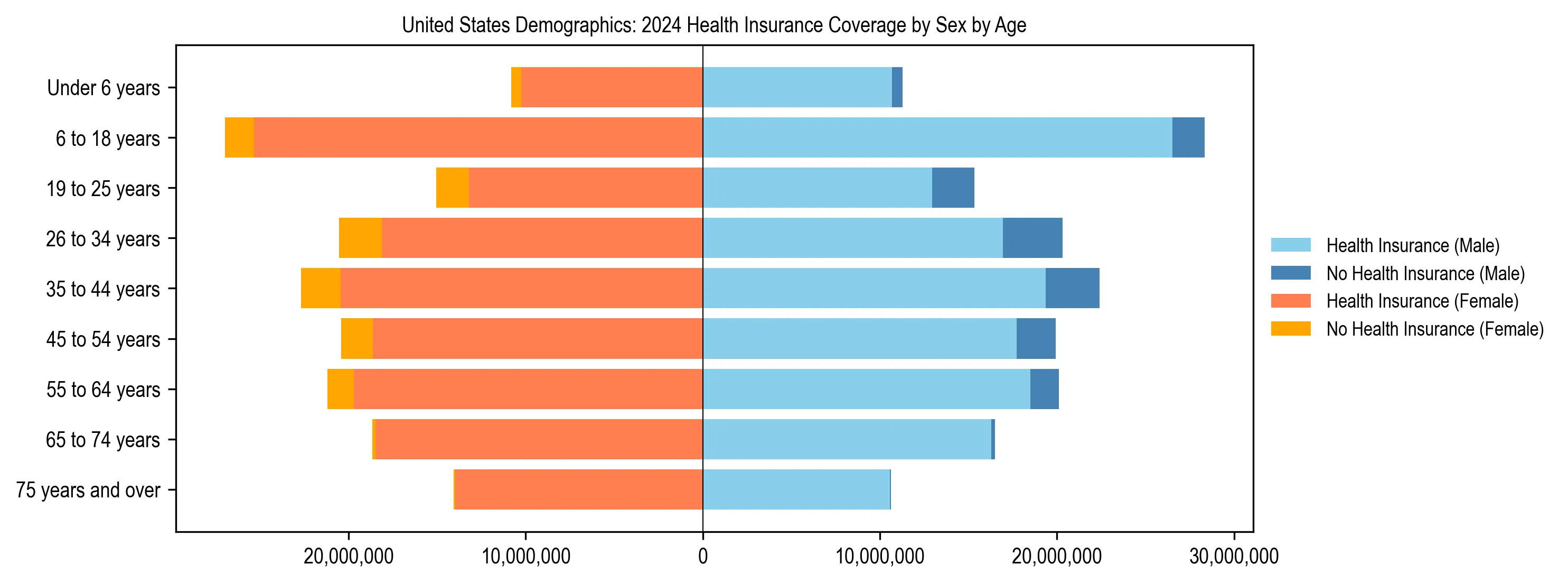
United States Uninsured Rates by Demographics
| Age Group | Male Uninsured % | Female Uninsured % |
|---|---|---|
| Under 18 | 6.1% | 5.9% |
| 18-34 years | 16.1% | 12.0% |
| 35-64 years | 10.9% | 8.6% |
| 65+ years | 0.9% | 0.8% |
United States Nativity & Citizenship Statistics (2024)
Citizenship Snapshot for United States
The following data details the citizenship status and nativity of the population in the United States, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- U.S. Citizenship Rate
- 92.8% (Native-born + Naturalized)
- Naturalized Citizens
- 25,837,975 (Foreign-born individuals who acquired citizenship)
- Non-Citizen Residents
- 24,396,883
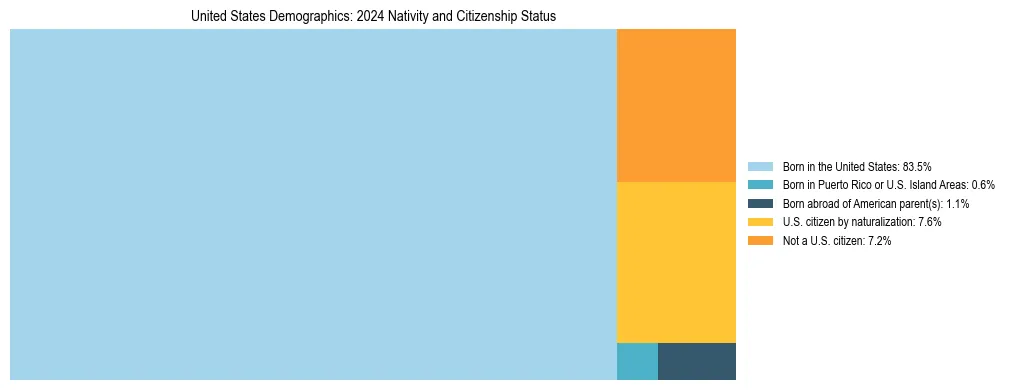
United States Nativity Distribution
| Nativity/Citizenship Status | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Born in the United States | 83.5% |
| Born in Puerto Rico or U.S. Island Areas | 0.6% |
| Born abroad of American parent(s) | 1.1% |
| U.S. citizen by naturalization | 7.6% |
| Not a U.S. citizen | 7.2% |
| Total U.S. Citizens | 92.8% |
United States Commuting & Transportation Statistics (2024)
Commuter Snapshot for United States
The following data details the commuting habits of the workforce in the United States, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Drove to Work (Car/Truck/Van)
- 78.4%
- Public Transportation Usage
- 3.7%
- Work From Home Rate
- 13.3%
- Total Workers Analyzed
- 165,360,450
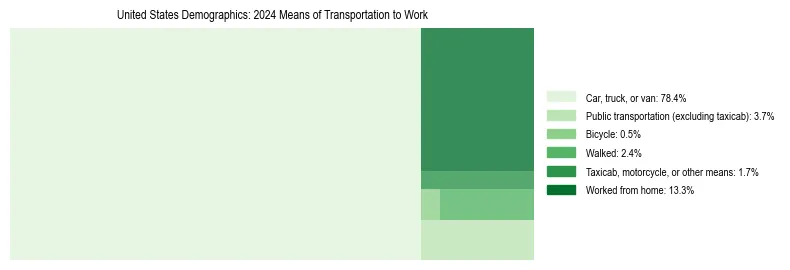
United States Commute Breakdown
| Transportation Method | Percentage | Number of Workers |
|---|---|---|
| Car, truck, or van | 78.4% | 129,643,168 |
| Public transportation | 3.7% | 6,097,425 |
| Bicycle | 0.5% | 803,184 |
| Walked | 2.4% | 4,048,560 |
| Taxicab, motorcycle, or other means | 1.7% | 2,741,742 |
| Worked from home | 13.3% | 22,026,371 |
| Total Workers | - | 165,360,450 |
United States Employment by Class of Worker (2024)
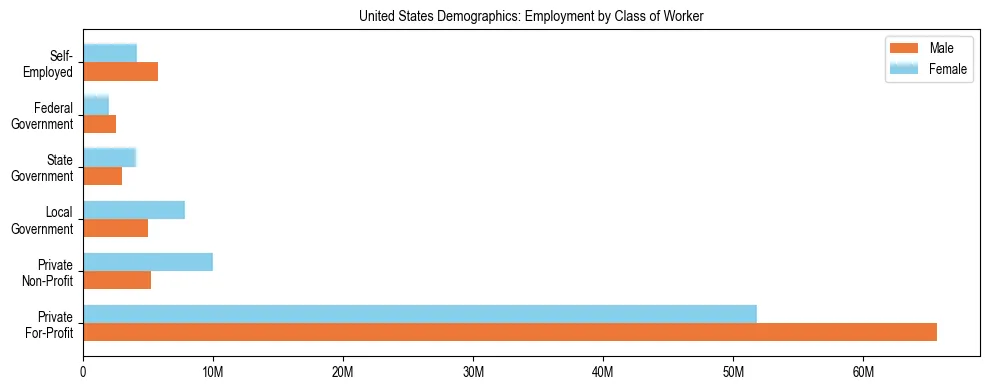
Workforce Snapshot for United States
The following statistics categorize the civilian employed population aged 16 and over in the United States by their employment sector, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Total Employed Civilian Population
- 167,292,666
- Private Sector (Profit & Non-Profit)
- Includes For-Profit and Non-Profit organizations
- Government Workers
- Includes Local, State, and Federal employees
- Self-Employed Workers
- Includes own not incorporated business workers
United States Employment Sector Breakdown
| Employment Class | Male Workers | Female Workers |
|---|---|---|
| Private For-Profit | 65,682,056 (39.3%) | 51,785,989 (31.0%) |
| Private Non-Profit | 5,235,213 (3.1%) | 9,976,641 (6.0%) |
| Government (All Levels) | 10,505,516 (6.3%) | 13,919,244 (8.3%) |
| • Local Government | 4,997,598 | 7,817,407 |
| • State Government | 2,972,539 | 4,058,397 |
| • Federal Government | 2,535,379 | 2,043,440 |
| Self-Employed | 5,743,285 (3.4%) | 4,127,989 (2.5%) |
Definitions: "Private sector" includes employees of for-profit and non-profit companies. "Government" includes all local, state, and federal employees. "Self-employed" refers to those operating their own unincorporated businesses.
United States Veteran Population & Service Statistics (2024)
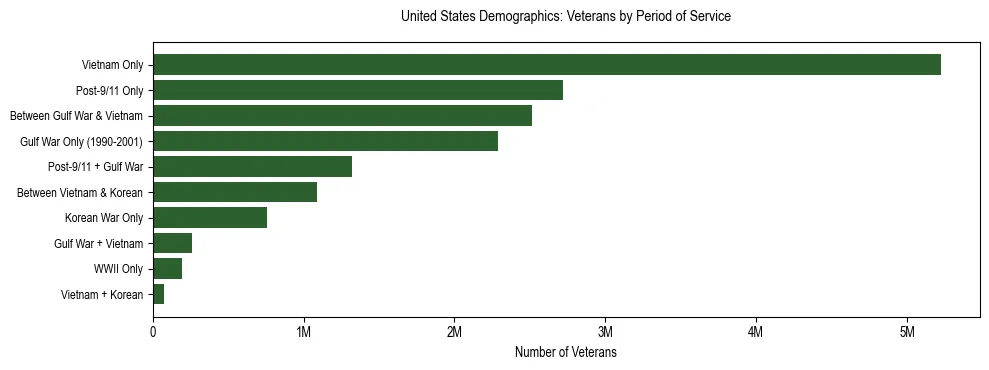
Veteran Community Snapshot for United States
The following data details the civilian veteran population aged 18 and over in the United States, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Total Civilian Veterans
- 16,569,149
- Primary Service Era
- Vietnam Era Only
5,221,921 veterans (31.5%)
United States Service Period Breakdown
| Period of Service | Number of Veterans | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Vietnam Era Only (August 1964 to April 1975) | 5,221,921 | 31.5% |
| Post-9/11 Only (September 2001 or later) | 2,721,701 | 16.4% |
| Between Gulf War and Vietnam Era | 2,511,442 | 15.2% |
| Gulf War Only (August 1990 to August 2001) | 2,288,705 | 13.8% |
| Post-9/11 and Gulf War (August 1990 to August 2001) | 1,320,312 | 8.0% |
| Between Vietnam Era and Korean War | 1,088,163 | 6.6% |
| Korean War Only (July 1950 to January 1955) | 760,295 | 4.6% |
| Gulf War and Vietnam Era | 262,446 | 1.6% |
| World War II Only (December 1941 to December 1946) | 195,123 | 1.2% |
| Vietnam Era and Korean War | 76,601 | 0.5% |
| Post-9/11, Gulf War, and Vietnam Era | 57,148 | 0.3% |
| Between Korean War and World War II | 39,260 | 0.2% |
| Korean War and World War II | 16,439 | 0.1% |
| Vietnam Era, Korean War, and World War II | 7,826 | 0.0% |
| Pre-World War II | 1,767 | 0.0% |
| Total Veterans | 16,569,149 | 100.0% |
Note: Periods of service include World War II (Dec 1941–Dec 1946), Korean War (Jul 1950–Jan 1955), Vietnam Era (Aug 1964–Apr 1975), Gulf War (Aug 1990–Aug 2001), and Post-9/11 (Sept 2001 or later). Veterans may have served in multiple eras.
United States Family Poverty & Income Statistics (2024)
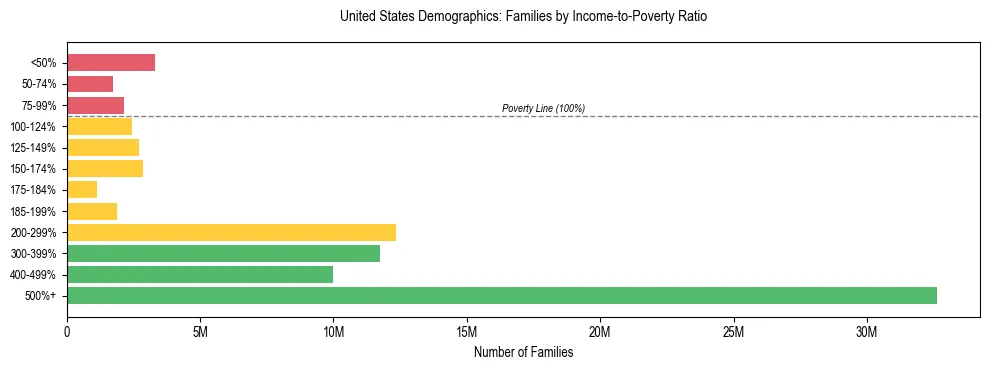
Family Economic Security Snapshot for United States
The following data categorizes families in the United States by their income relative to the federal poverty threshold, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Families Below Poverty Line (<100%)
- 8.5% (7,231,051 families)
- Families Near Poverty (100-199%)
- 27.5% (23,395,492 families)
- Families with Secure Income (200%+)
- 64.0% (54,339,996 families)
United States Income-to-Poverty Ratio Breakdown
| Income-to-Poverty Ratio Category | Number of Families | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Below 50% of Poverty | 3,322,818 | 3.9% |
| 50-74% of Poverty | 1,744,209 | 2.1% |
| 75-99% of Poverty | 2,164,024 | 2.5% |
| 100-124% of Poverty | 2,461,798 | 2.9% |
| 125-149% of Poverty | 2,724,678 | 3.2% |
| 150-174% of Poverty | 2,855,622 | 3.4% |
| 175-184% of Poverty | 1,140,106 | 1.3% |
| 185-199% of Poverty | 1,882,605 | 2.2% |
| 200-299% of Poverty | 12,330,683 | 14.5% |
| 300-399% of Poverty | 11,741,986 | 13.8% |
| 400-499% of Poverty | 9,990,487 | 11.8% |
| 500%+ of Poverty | 32,607,523 | 38.4% |
| Total Families | 84,966,539 | 100.0% |
Definition: The "Income-to-Poverty Ratio" measures a family's income against the federal poverty threshold. A ratio below 1.00 means the family is in poverty. Ratios between 1.00 and 1.99 indicate low income ("near poverty"), while ratios of 2.00 or higher suggest greater economic security.
United States SNAP/Food Stamps Statistics (2024)
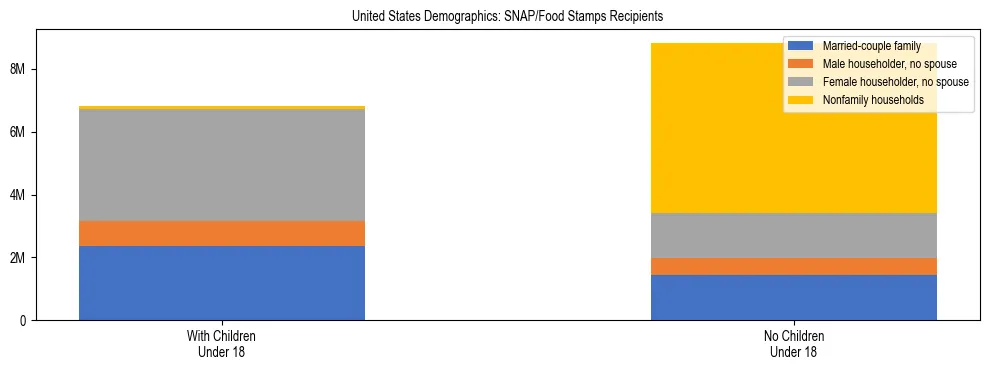
SNAP Participation Snapshot for United States
The following data details household participation in the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) in the United States, based on U.S. Census Bureau 2024 ACS Estimates.
- Total Households Receiving SNAP
- 15,632,675 (11.78% of all households)
- Recipient Households with Children
- 6,812,070 (43.58% of recipients)
- Total Households Analyzed
- 132,737,146
United States SNAP Recipient Demographics
| Household Type | With Children Under 18 | No Children Under 18 |
|---|---|---|
| Married-Couple Family | 2,363,868 (15.12%) | 1,423,294 (9.10%) |
| Male Householder, No Spouse | 790,094 (5.05%) | 544,937 (3.49%) |
| Female Householder, No Spouse | 3,571,051 (22.84%) | 1,457,200 (9.32%) |
| Nonfamily Households | 87,057 (0.56%) | 5,395,174 (34.51%) |
About this data: The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) provides food assistance to low-income families. Households with children often face higher participation rates due to eligibility guidelines prioritizing child nutrition. "Nonfamily households" typically refer to individuals living alone or with unrelated roommates.